Primena impregnisanog biouglja proizvedenog iz sojinih ljuspica u procesu obezbojavanja boje
Glavni sadržaj članka
Apstrakt
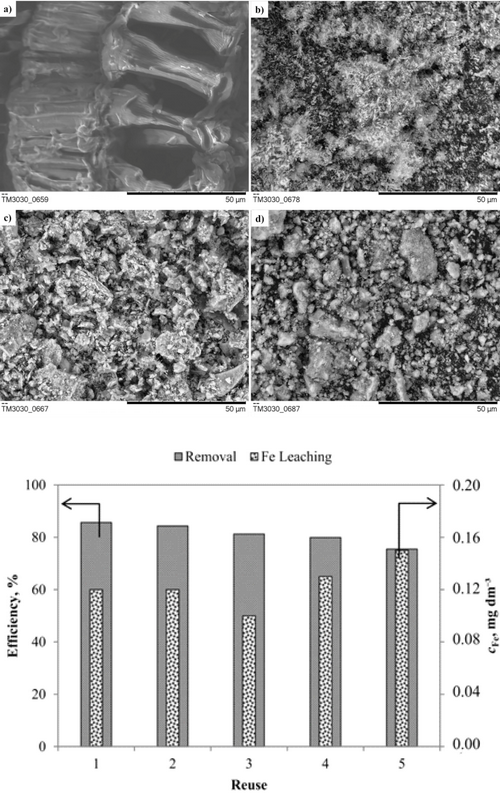
U cilju moguće valorizacije, otpadne sojine ljuspice (engl. waste soybean hulls, OSLj) su ispitivane kao nosači jona Fe, u dve različite forme: sirovoj i karbonizovanoj (engl. biocarbon, BU). Impregnacija jonima Fe(III) je implementirana radi sinteze heterogenih Fenton katalizatora (Fe-OSLj i Fe-BU) za obezbojavanje vodenog rastvora Reactive Blue 4 (RB4) boje. Karakterizacija materijala je pokazala porast specifične površine zbog dekompozicije konstituenata OSLj tokom karbonizacije (prilikom dobijanja BU) i termalne aktivacije (prilikom dobijanja Fe-OSLj i Fe-BU), gde su dobijeni katalizatori visoke mezoporoznosti sa hematitom kao aktivnom fazom za odvijanje Fentonove reakcije. Među pripremljenim materijalima, Fe-OSLj je pokazao značajnu sposobnost produkcije •OH radikala u kiseloj sredini. Dalje, optimizacija heterogenog Fenton procesa je izvedena primenom metodologije odzivnih površina (engl. Respose Surface Methodology, RSM), gde su redukovanim modelom izdvojeni sledeći uslovi reakcije: 3 mM H2O2, 100 mg Fe-OSLj, vreme reakcije od 180 min, pri konstantnim vrednostima pH = 3, koncentracije boje od 50 mg RB4 dm-3 i na sobnoj temperaturi. Postignuto je 88,7% i 66,8% obezbojavanja i mineralizacije RB4 boje, redom; Fe-OSLj je pokazao veliku stabilnost, a reakcioni intermedijeri formirani tokom oksidacionog procesa su imali mali inhibitorni efekat na Vibrio fischeri bakterije.
Detalji članka
Broj časopisa
Rubrika

Ovaj rad je pod Creative Commons Aуторство-Nekomercijalno-Bez prerade 4.0 Internacionalna licenca.
Kada je rukopis prihvaćen za objavlјivanje, autori prenose autorska prava na izdavača. U slučaju da rukopis ne bude prihvaćen za štampu u časopisu, autori zadržavaju sva prava.
Na izdavača se prenose sledeća prava na rukopis, uklјučujući i dodatne materijale, i sve delove, izvode ili elemente rukopisa:
- pravo da reprodukuje i distribuira rukopis u štampanom obliku, uklјučujući i štampanje na zahtev;
- pravo na štampanje probnih primeraka, reprint i specijalnih izdanja rukopisa;
- pravo da rukopis prevede na druge jezike;
- pravo da rukopis reprodukuje koristeći fotomehanička ili slična sredstva, uklјučujući, ali ne ograničavajući se na fotokopiranje, i pravo da distribuira ove kopije;
- pravo da rukopis reprodukuje i distribuira elektronski ili optički koristeći sve nosioce podataka ili medija za pohranjivanje, a naročito u mašinski čitlјivoj/digitalizovanoj formi na nosačima podataka kao što su hard disk, CD-ROM, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), mini disk, trake sa podacima, i pravo da reprodukuje i distribuira rukopis sa tih prenosnika podataka;
- pravo da sačuva rukopis u bazama podataka, uklјučujući i onlajn baze podataka, kao i pravo prenosa rukopisa u svim tehničkim sistemima i režimima;
- pravo da rukopis učini dostupnim javnosti ili zatvorenim grupama korisnika na osnovu pojedinačnih zahteva za upotrebu na monitoru ili drugim čitačima (uklјučujući i čitače elektonskih knjiga), i u štampanoj formi za korisnike, bilo putem interneta, onlajn servisa, ili putem internih ili eksternih mreža.
Kako citirati
Reference
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ, Pinjari DV, Mahamuni NM, Pandit AB. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manage. 2016; 182: 351–366. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.090
Gözmen B, Kayan B, Gizir M, Heresnov A. Oxidative degradations of reactive blue 4 dye by different advanced oxidation methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009; 168: 129–136. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.011
Hassan H, Hameed BH. Fe-Natural Zeolite as Highly Active Heterogeneous Catalyst in Decolorization of Reactive Blue 4. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2020; 11: 133–137. https://dx.doi.org/10.18178/ijesd.2020.11.3.1239
Fatma NY, Riyanti F, Hariani PL, Nurbaiti B. Synthesis of chitosan/alumina composite by sol gel method for adsorption of procion blue MX-R dye from wastewater songket industry. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019; 1282: 012080. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1282/1/012080
da Silva RG, de Andrade AR. Degradation of the Dye Reactive Blue 4 by Coupled Photoassisted Electrochemistry at DSA®-Type Electrode. J. Brazil. Chem. Soc. 2016; 27: 857–865. http://dx.doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20150338
Tomin MB, Kulic A, Kerkez D, Prica M, Rapajic S, Pilipovic DT, Pesic V. Reactive dye degradation using Fe-loaded bentonite as a Fenton-like catalyst: From process optimization to effluent acute toxicity. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2017; 26: 8184–8198. https://www.prt-parlar.de/download_feb_2017/
Zhang M, Dong H, Zhao L, Wang D, Meng D. A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019; 670: 110–121. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.180
Eloussaief M, Hamza W, Ghorbali G, Kallel N, Benzina M. Fe-Rich Aragonite Concretion Applied to Industrial Dye Purification Using Fenton and Photo-Fenton Technologies. Waste Biomass Valori. 2021; 12: 3303-3313. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01228-6
Wang N, Zheng T, Zhang G, Wang P. A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016; 4: 762–787. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.12.016
Javaid R, Qazi UY. Catalytic oxidation process for the degradation of synthetic dyes: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019; 16: 2066. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16112066
Zhu Y, Zhu R, Xi Y, Zhu J, Zhu G, He H. Strategies for enhancing the heterogeneous Fenton catalytic reactivity: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019; 255: 117739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.05.041
Bello M, Raman AA, Asghar A. A review on approaches for addressing the limitations of Fenton oxidation for recalcitrant wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019; 126: 119-140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.03.028
Nidheesh PV. Heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the abatement of organic pollutants from aqueous solution: A review. RSC Adv. 2015; 5: 40552–40577. https://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c5ra02023a
Wang J, Bai Z. Fe-based catalysts for heterogeneous catalytic ozonation of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017; 312: 79–98. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.118
Girish CR. Various impregnation methods used for the surface modification of the adsorbent: A review. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018; 7: 330–334. https://dx.doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i4.7.20571
Elías VR, Rodriguez PAO, Vaschetto EG, Pecchi GA, Huck-Iriart C, Casuscelli SG, Eimer GA. Tailoring the stability and photo-Fenton activity of Fe-modified nanostructured silicates by tuning the metal speciation from different synthesis conditions. Mol. Catal. 2020; 481: 110217. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.012
Setiawan WK, Chiang KY. Crop Residues as Potential Sustainable Precursors for Developing Silica Materials: A Review. Waste Biomass Valori. 2020; 2207-2236. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01126-x
Campbell-Johnston K, Vermeulen WJV, Reike D, Brullot S. The Circular Economy and Cascading: Towards a Framework. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. X. 2020; 7: 100038. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rcrx.2020.100038
Xiang W, Zhang X, Chen J, Zou W, He F, Hu X, Tsang DCW, Ok YS, Gao B. Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere. 2020; 252: 126539. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126539
Enaime G, Baçaoui A, Yaacoubi A, Lübken M. Biochar for wastewater treatment-conversion technologies and applications. Appl. Sci. 2020; 10: 3492. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/app10103492
Pan X, Gu Z, Chen W, Li Q. Preparation of biochar and biochar composites and their application in a Fenton-like process for wastewater decontamination: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021; 754: 142104. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142104
Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Statistical Release PO16: Realized production of wheat and early fruit and expected yields of late crops, fruit and grapes, 2020. Agric. Stat. 2020; 262: 1-2. ISSN 0353-9555
Barros PJR, Ascheri DPR, Santos MLS, Morais CC, Ascheri JLR, Signini R, dos Santos DM, de Campos AJ, Devilla IA. Soybean hulls: Optimization of the pulping and bleaching processes and carboxymethyl cellulose synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020; 144: 208–218. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.074
Liu H-M, Li H-Y. Application and Conversion of Soybean Hulls. In: Kasai M, ed. Soybean - The Basis of Yield, Biomass and Productivity. IntechOpen; 2017: 111–132. https://dx.doi.org/10.5772/66744
Qing Q, Guo Q, Zhou L, Gao X, Lu X, Zhang Y. Comparison of alkaline and acid pretreatments for enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean hull and soybean straw to produce fermentable sugars. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017; 109: 391–397. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.08.051
Neto WPF, Silvério HA, Dantas NO, Pasquini D. Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from agro-industrial residue - Soy hulls. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013; 42: 480–488. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.06.041
Toro-Trochez JL, Carrillo-Pedraza ES, Bustos-Martínez D, García-Mateos FJ, Ruiz-Rosas RR, Rodríguez-Mirasol J, Cordero T. Thermogravimetric characterization and pyrolysis of soybean hulls. Bioresour. Technol. Reports. 2019; 6: 183–189. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.02.009
Herde ZD, Dharmasena R, Sumanasekera G, Tumuluru JS, Satyavolu J. Impact of hydrolysis on surface area and energy storage applications of activated carbons produced from corn fiber and soy hulls. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2020; 3: 19–28. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.crcon.2019.12.002
Bečelić-Tomin M, Kulić A, Kerkez Đ, Pilipović DT, Pešić V, Dalmacija B. Synthesis of impregnated bentonite using ultrasound waves for application in the Fenton process. Clay Miner. 2018; 53: 203–212. https://dx.doi.org/10.1180/clm.2018.14
Xiao C, Li J, Zhang G. Synthesis of stable burger-like α-Fe2O3 catalysts: Formation mechanism and excellent photo-Fenton catalytic performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2018; 180: 550–559. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.127
Trovó AG, Nogueira RFP, Agüera A, Fernandez-Alba AR, Malato S. Degradation of the antibiotic amoxicillin by photo-Fenton process - Chemical and toxicological assessment. Water Res. 2011; 45: 1394–1402. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.10.029
Milidrag GP, Prica M, Kerkez D, Dalmacija B, Kulic A, Pilipovic DT, Tomin MB. A comparative study of the decolorization capacity of the solar-assisted Fenton process using ferrioxalate and Al, Fe-bentonite catalysts in a parabolic trough reactor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018; 93: 436–449. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.08.015
Balint T, Chang BP, Mohanty AK, Misra M. Underutilized Agricultural Co-Product as a Sustainable Biofiller for Polyamide 6,6: Effect of Carbonization Temperature. Molecules. 2020; 25: 1455. https://dx.doi.org/doi:10.3390/molecules25061455
Wu Q, Ouyang J, Xie K, Sun L, Wang M, Lin C. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis and visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of Fe-incorporated TiO2 nanotube array photocatalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012; 199–200: 410–417. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.031
Nandiyanto ABD, Oktiani R, Ragadhita R. How to read and interpret ftir spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2019; 4: 97–118. https://dx.doi.org/10.17509/ijost.v4i1.15806
Chen Y, Shi J, Du Q, Zhang H, Cui Y. Antibiotic removal by agricultural waste biochars with different forms of iron oxide. RSC Adv. 2019; 9: 14143–14153. https://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c9ra01271k
Wang QJ, Liu RJ, Shen XQ, Wu DM, Li HH. Fabrication and methyl blue adsorption kinetics of α-Fe2O3 nanotubes by electrospinning. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013; 699: 302–307. https://dx.doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.699.302
Galan J, Trilleras J, Zapata PA, Arana VA, Grande-Tovar CD. Optimization of chitosan glutaraldehyde-cross linked beads for reactive blue 4 anionic dye removal using a surface response methodology. Life. 2021; 11: 1–20. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/life11020085
Zhao L, Lin ZR, Ma XH, Dong, YH. Catalytic activity of different iron oxides: Insight from pollutant degradation and hydroxyl radical formation in heterogeneous Fenton-like systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018; 352: 343–351. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.035
Becelic-Tomin M, Dalmacija B, Rajic L, Tomasevic D, Kerkez D, Watson M, Prica M. Degradation of anthraquinone dye reactive blue 4 in pyrite ash catalyzed fenton reaction. Sci. World J. 2014; 234654. https://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/234654
Schneider JT, Firak DS, Ribeiro RR, Peralta-Zamora P. Use of scavenger agents in heterogeneous photocatalysis: truths, half-truths, and misinterpretations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020; 22: 15723–15733. https://dx.doi.org/10.1039/d0cp02411b
Stupar SL, Grgur BN, Radišić MM, Onjia AE, Ivanković ND, Tomašević AV, Mijin D. Oxidative degradation of Acid Blue 111 by electro-assisted Fenton process. J. Water Process Eng. 2020; 36: 101394. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101394