Tehnologija elektrokoagulacije kao nova i napredna tehnologija za buduće izazove u postrojenjima za prečišćavanje vode u industriji čelika Stručni rad
Glavni sadržaj članka
Apstrakt
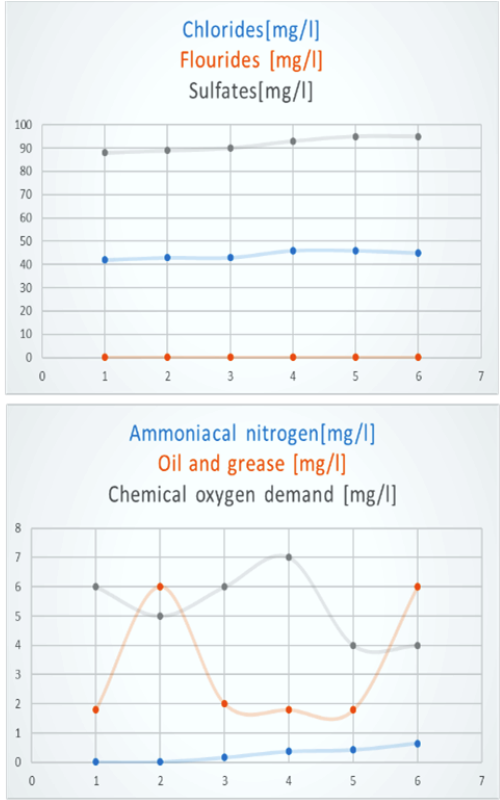
Voda je osnovna životna potreba, i može se činiti nezamislivim zamisliti život bez nje. Uticaj na životnu sredinu, zajedno sa socijalnim i ekonomskim uticajem konvencionalnih i tradicionalnih tretmana vode u postrojenjima u industriji čelika i neizbežnom činjenicom nestašice vode, vode i pokreću prelazak na novu paradigmu u tretmanima vode. Ovo istraživanje je imalo za cilj da ispita efikasnost procesa elektrokoagulacije i jedinice za flotaciju rastvorenog vazduha za uklanjanje različitih nečistoća u vodi iz fabrike za proizvodnju čelika. Tokom proteklih decenija, elektrokoagulacija je prihvaćena kao efikasna i obećavajuća alternativna tehnologija u oblasti prečišćavanja vode. Elektrokoagulacija tehnika je usko povezana sa hemijskom koagulacijom, koja uključuje snabdevanje koagulantnih jona primenom električne struje na žrtvenu anodu (napravljenu od aluminijuma ili gvožđa) smeštenu u procesni rezervoar. Glavni fokus istraživanja je stavljen na ukupne rastvorene materije i provodljivost vode. U tradicionalnim sistemima, ukupne rastvorene materije i provodljivost vode su jedan od parametara na koje ne mogu uticati hemijske jedinice za doziranje. Specifični cilj je bio da se razumeju parametri koji utiču na efikasnost procesa elektrokoagulacije, tako da se utiče na ukupan sadržaj rastvorenih materija i smanjenje zaostalih neorganskih i organskih nečistoća, održavajući neophodnu ravnotežu vode.
Detalji članka
Broj časopisa
Rubrika

Ovaj rad je pod Creative Commons Autorstvo 4.0 Internacionalna licenca.
Kada je rukopis prihvaćen za objavlјivanje, autori prenose autorska prava na izdavača. U slučaju da rukopis ne bude prihvaćen za štampu u časopisu, autori zadržavaju sva prava.
Na izdavača se prenose sledeća prava na rukopis, uklјučujući i dodatne materijale, i sve delove, izvode ili elemente rukopisa:
- pravo da reprodukuje i distribuira rukopis u štampanom obliku, uklјučujući i štampanje na zahtev;
- pravo na štampanje probnih primeraka, reprint i specijalnih izdanja rukopisa;
- pravo da rukopis prevede na druge jezike;
- pravo da rukopis reprodukuje koristeći fotomehanička ili slična sredstva, uklјučujući, ali ne ograničavajući se na fotokopiranje, i pravo da distribuira ove kopije;
- pravo da rukopis reprodukuje i distribuira elektronski ili optički koristeći sve nosioce podataka ili medija za pohranjivanje, a naročito u mašinski čitlјivoj/digitalizovanoj formi na nosačima podataka kao što su hard disk, CD-ROM, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), mini disk, trake sa podacima, i pravo da reprodukuje i distribuira rukopis sa tih prenosnika podataka;
- pravo da sačuva rukopis u bazama podataka, uklјučujući i onlajn baze podataka, kao i pravo prenosa rukopisa u svim tehničkim sistemima i režimima;
- pravo da rukopis učini dostupnim javnosti ili zatvorenim grupama korisnika na osnovu pojedinačnih zahteva za upotrebu na monitoru ili drugim čitačima (uklјučujući i čitače elektonskih knjiga), i u štampanoj formi za korisnike, bilo putem interneta, onlajn servisa, ili putem internih ili eksternih mreža.
Kako citirati
Reference
[1] Araújo CVM, Nascimento RB., Oliveira CA., Strotmann UJ, Da Silva EM. The use of Microtox® to assess toxicity removal of industrial effluents from the industrial district of Camaçari (BA, Brazil). Chemosphere. 2005; 58(9):1277-1281 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.036
[2] Heidmann I., Calmano W. Removal of Zn(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Ag(I) and Cr(VI)present in aqueous solutions by aluminium electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater. 2008; 152: 934-941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.068
[3] Akbal F., Camci S. Copper, chromium and nickel removal from metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination. 2011; 269: 214-222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.001
[4] Akbal F., Camci S. Treatment of metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. 2012; 31: 340-350 https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10546
[5] Kabuk HA., Avsar Y., Ilhan F., Ulucan K. Comparison of pH adjustment and electrocoagulation processes on treatability of metal plating wastewater. Sep Sci Technol. 2014; 49: 613-618. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.839705
[6] Al-Shannag M, Al-Qodah Z, Bani-Melhem K., Qtaishat MR, Alkasrawi M. Heavy metal ions removal from metal plating wastewater using electrocoagulation: kinetic study and process performance. Chem Eng J. 2015; 260: 749-756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.035
[7] Hunsom M, Pruksathorn K, Damronglerd S, Vergnes H, Duverneuil P. Electrochemical treatment of heavy metals (Cu2+, Cr6+, Ni2+) from industrialeffluent and modeling of copper reduction. Water Res. 2005; 39: 610-616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.10.011
[8] David V, Ortiz JM, Vicente G, Eduardo E, Vicente M, Antonio A. Electrocoagulation of wastewater from almond industry. Chemosphier. 2011; 84: 1290-1295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.032
[9] Lancaster M. Green Chemistry, An Introductory Text. Royal Society of Chemistry, Org Proc Res Dev. 2004: 8, 2: 299-300. https://doi.org/10.1021/op049976c
[10] Jianbo L., Peng Z., Jie L. Electrocoagulation technology for water purification: An update review on reactor design and some newly concerned pollutants removal. J Environ Manag. 2021; 84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113259
[11] Bazrafshan E, Mohammadi L, Ansari-Moghaddam A, Mahvi AH. Heavy metals removal from aqueous environments by electro¬coagulation process- a systematic review. J Environ Health Sci. 2015; 13: 74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0233-8
[12] Van der Bruggen B, Everaert K, Wilms D, Vandecasteele C. Application of nanofiltration for removal of pesticides, nitrate and hardness from ground water: rejection properties and economic evaluation. J Membr Sci. 2001; 193: 239-248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(01)00517-8
[13] Chou WL, Wang CT, Huang KY. Effect of operating parameters on indium (III) ion removal by iron electrocoagulation and evaluation of specific energy consumption. J Hazard Mater. 2009; 167(1-3):467-474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.008
[14] DrouicheN, Ghaffour N, Lounici H, Mameri M. Electrocoagulation of chemical mechanical polishing wastewater. Desalination. 2007; 214: 31-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.11.009
[15] Hyun Kim T, Park C, Shin E-B, Kim S. Decolorization of disperse and reactive dyes by continuous electrocoagulation process. Desalination. 2002; 150: 165-175, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00941-4
[16] Holt PK, Barton G, Wark M, Mitche C. A quantitative comparison between chemical dosing and electrocoagulation. Colloid Surf A. 2002; 211: 233-248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757%2802%2900285-6
[17] Mollah MYA, Schennach R, Parga JR, Cocke DL. Electrocoagulation (EC) science and applications. J Hazard Mater. 2001; B84: 29-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00176-5
[18] Hu CY, Lo SL, Kuan WH. Effects of co-existing anions on fluoride removal in electrocoagulation (EC) process using aluminum electrodes. Water Res.2003; 37(18): 4513-4523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00378-6
[19] Can OT, Kobya M, Demirbas E, Bayramoglu M. Treatment of the textile wastewater by combined electrocoagulation. Chemosphere. 2006; 62: 181-187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.022
[20] Hasson D, Lumelsky V, Greenberg G, Pinhas Y, Semiat R. Development of the electrochemical scale removal technique for desalination applications. Desalination 2008; 230: 329-334 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.01.004.
[21] Hakizimana JN, Gourich B, Chafi M, Stiriba Y, Vial C, Drogui P, Naja J. Electrocoagulation process in water treatment: a review of electrocoagulation modeling approaches. Desalination 2017; 404: 1-21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.10.011.
[22] Moussa DT, El-Naas MH, Nasser M, Al-Marri MJ. A comprehensive review of electrocoagulation for water treatment: potentials and challenges. J EnvironManage. 2017; 186: 24-41, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.10.032
[23] Lin SH, Wu CL. Electrochemical removal of nitrite and ammonia for aquaculture. Water Res. 1996; 30: 715-721, https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(95)00208-1
[24] Malakootian M, Mansoorian HJ, Moosazadeh M. Performance evaluation of electrocoagulation process using iron-rod electrodes for removing hardness from drinking water. Desalination 2010; 255: 67-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.01.015