Uticaj Ringerovog rastvora na habanje vakuumski tretiranog koštanog cementa od poli(metil metakrilata) u kontaktu sa AISI 316L nerđajućim čelikom pri linearno naizmeničnom kretanju Naučni rad
Glavni sadržaj članka
Apstrakt
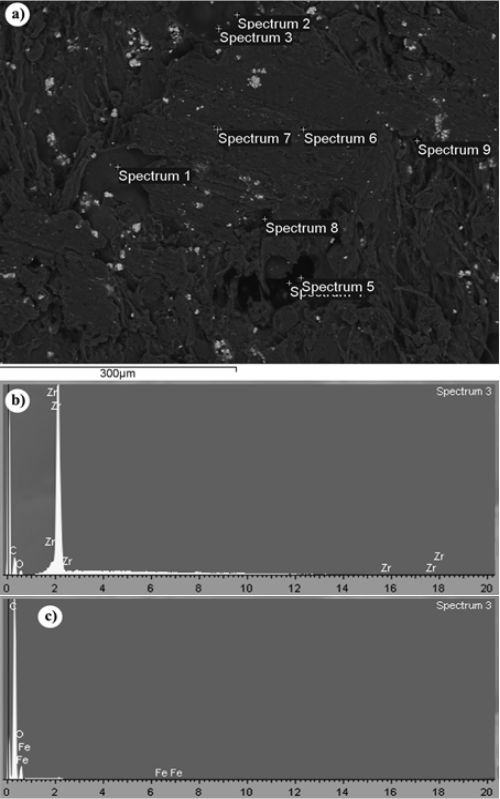
U radu su prikazane mikrostrukturne karakteristike i ponašanje PMMA koštanog cementa mešanog u vakuumu, pri kontaktu sa AISI 316L nerđajućim čelikom, sa mikro opterećenjima i analiziran je uticaj prisustva Ringerovog rastvora na habanje u odnosu na suvi kontakt. Promena sile nije značajno uticala na faktor habanja dok je povećanje brzine klizanja uslovilo značajan porast faktora habanja, naročito u slučaju suvog kontakta. Faktori habanja su u proseku bili veći za klizanje u Ringerovom rastvoru od suvog kontakta. Uočena je značajna fragmentacija tragova habanja, nepravilnog oblika, sa izlomljenim ivicama, što je bilo više naglašeno pri suvom kontaktu. U tragovima habanja se uočavaju brojni otvori i šupljine, koji se ne šire u dubinu materijala. Veća opterećenja su uzrokovala uniformnije i manje fragmentirane tragove habanja. Uočeno je abrazivno i adhezivno habanje i tragovi plastične deformacije, kao i zamorno i erozivno habanje. Zamorne pukotine su se širile u pravcu normalnom na pravac klizanja. Fina mreža tankih površinskih lomnih pukotina je uočena na površini tragova habanja, posebno u slučaju suvog kontakta. Rezultati su značajni kao doprinos razumevanju inicijacije pukotina i mehanizmima njihovog razvoja na površini PMMA koštanog cementa, uključujući i sinergijske efekte fiziološke okoline s aspekta nestacionarnog ponašanja i modela razvoja pukotina kod PMMA.
Detalji članka
Broj časopisa
Rubrika

Ovaj rad je pod Creative Commons Aуторство-Nekomercijalno-Bez prerade 4.0 Internacionalna licenca.
Kada je rukopis prihvaćen za objavlјivanje, autori prenose autorska prava na izdavača. U slučaju da rukopis ne bude prihvaćen za štampu u časopisu, autori zadržavaju sva prava.
Na izdavača se prenose sledeća prava na rukopis, uklјučujući i dodatne materijale, i sve delove, izvode ili elemente rukopisa:
- pravo da reprodukuje i distribuira rukopis u štampanom obliku, uklјučujući i štampanje na zahtev;
- pravo na štampanje probnih primeraka, reprint i specijalnih izdanja rukopisa;
- pravo da rukopis prevede na druge jezike;
- pravo da rukopis reprodukuje koristeći fotomehanička ili slična sredstva, uklјučujući, ali ne ograničavajući se na fotokopiranje, i pravo da distribuira ove kopije;
- pravo da rukopis reprodukuje i distribuira elektronski ili optički koristeći sve nosioce podataka ili medija za pohranjivanje, a naročito u mašinski čitlјivoj/digitalizovanoj formi na nosačima podataka kao što su hard disk, CD-ROM, DVD, Blu-ray Disc (BD), mini disk, trake sa podacima, i pravo da reprodukuje i distribuira rukopis sa tih prenosnika podataka;
- pravo da sačuva rukopis u bazama podataka, uklјučujući i onlajn baze podataka, kao i pravo prenosa rukopisa u svim tehničkim sistemima i režimima;
- pravo da rukopis učini dostupnim javnosti ili zatvorenim grupama korisnika na osnovu pojedinačnih zahteva za upotrebu na monitoru ili drugim čitačima (uklјučujući i čitače elektonskih knjiga), i u štampanoj formi za korisnike, bilo putem interneta, onlajn servisa, ili putem internih ili eksternih mreža.
Kako citirati
Reference
Boote AT, Bigsby RJ, Deehan DJ, Rankin KS, Swailes DC, Hyde PJ. Does vacuum mixing affect diameter shrinkage of a PMMA cement mantle during in vitro cemented acetabulum implantation? Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part H.2021; 235: 133–140.
Lewis G. Viscoelastic properties of injectable bone cements for orthopaedic applications: State-of-the-art review. J Biomed Mater Res, Part B. 2011; 98B(1): 171-191.
Stojkovic M, Milovanovic J, Vitkovic N, Trajanovic M, Grujovic N, Milivojevic V, Milisavljevic S, Mrvic S. Reverse modeling and solid free-form fabrication of sternum implant. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2010; 33(3): 243-250.
Garcés GA, Rojas VH, Bravo C, Sampaio CS. Shear bond strength evaluation of metallic brackets bonded to a CAD/CAM PMMA material compared to traditional prosthetic temporary materials: an in vitro study. Dental Press J Orthod. 2020; 25(3): 31-38.
Reyes-Sevilla M, Kuijs RH, Werner A, Kleverlaan CJ, Lobbezoo F. Comparison of wear between occlusal splint materials and resin composite materials. J Oral Rehabil. 2018; 45(7): 539-544.
Zivic F, Babic M, Grujovic N, Mitrovic S, Favaro G, Caunii M. Effect of vacuum-treatment on deformation properties of PMMA bone cement. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012; 5(1): 129-138.
Kraaij G, Zadpoor AA, Tuijthof GJM, Dankelman J, Nelissen RGHH, Valstar ER. Mechanical properties of human bone–implant interface tissue in aseptically loose hip implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014; 38: 59-68.
Wimhurst JA, Brooks RA, Rushton N. The effects of particulate bone cements at the bone-implant interface. J Bone Jt Surg. 2001; 83-B(4): 588-592.
Sinnett-Jones PE, Browne M, Moffat AJ, Jeffers JRT, Saffari N, Buffière J-Y, Sinclair I. Crack initiation processes in acrylic bone cement. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009; 89A(4): 1088-1097.
Nguyen NC, Maloney WJ, Dauskardt RH. Reliability of PMMA bone cement fixation: fracture and fatigue crack-growth behaviour. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1997; 8(8): 473-483.
Shih C-C, Shih C-M, Su Y-Y, Lin S-J. Potential risk of sternal wires. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004; 25(5): 812-818.
Geringer J, Pellier J, Cleymand F, Forest B. Atomic force microscopy investigations on pits and debris related to fretting-corrosion between 316L SS and PMMA. Wear. 2012; 292-293: 207-217.
Koistinen AP, Korhonen H, Kröger H, Lappalainen R. Interfacial sliding properties of bone screw materials and their effect on screw fixation strength. J Appl Biomater Func. 2014; 12(2): 90-96.
Takamizawa T, Barkmeier W, Tsujimoto A, Scheidel D, Erickson R, Latta M, Miyazaki M. Mechanical Properties and Simulated Wear of Provisional Resin Materials. Oper. 2015; 40(6): 603-613.
Alexeev AA, Bolshev KN, Ivanov VA, Syromyatnikova AS, Bolshakov AM, Andreev AS. Experimental Study of Crack Branching Velocity in Polymers. Inorg Mater. 2019; 55(15): 1476-1480.
Koch S, Meunier M, Hopmann C, Alperstein D. A combined experimental and computational study of environmental stress cracking of amorphous polymers. Polym Adv Technol. 2020; 31(2): 297-308.
Zivic F, Babic M, Mitrovic S, Vencl A. Continuous control as alternative route for wear monitoring by measuring penetration depth during linear reciprocating sliding of Ti6Al4V alloy. J Alloys Compd. 2011; 509(19): 5748-5754.
Arnold JC, Venditti NP. Effects of environment on the creep properties of a poly(ethylmethacrylate) based bone cement. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2001; 12(8): 707-717.
Myshkin NK, Pesetskii SS, Grigoriev AY. Polymer Tribology: Current State and Applications. Tribol Ind. 2015; 37(3): 284-290.
Tiainen V. Amorphous carbon as a bio-mechanical coating — mechanical properties and biological applications. Diamond Relat Mater. 2001; 10(2): 153-160.
Gorham DA, Salman AD, Pitt MJ. Static and dynamic failure of PMMA spheres. Powder Technol. 2003; 138(2-3): 229-238.
Pulos GC, Knauss WG. Nonsteady crack and craze behavior in PMMA under cyclical loading: I. Experimental preliminaries. Int J Fract. 1998; 93(1/4): 145-159.
Etienne S, Becker C, Ruch D, Grignard B, Cartigny G, Detrembleur C, Calberg C, Jerome R. Effects of incorporation of modified silica nanoparticles on the mechanical and thermal properties of PMMA. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2007; 87(1): 101-104.
Geringer J, Atmani F, Forest B. Friction–corrosion of AISI 316L/bone cement and AISI 316L/PMMA contacts: Ionic strength effect on tribological behaviour. Wear. 2009; 267(5-8): 763-769.
Munir S, Walsh WR. The Quantification of Corrosion Damage for Pre-stressed Conditions: A Model Using Stainless Steel. Journal of Bio- and Tribo-Corrosion. 2016; 2(1): 4.
Ayre WN, Denyer SP, Evans SL. Ageing and moisture uptake in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) bone cements. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014; 32: 76-88.
Savio JA, Overcamp LM, Black J. Size and shape of biomaterial wear debris. Clin Mater. 1994; 15(2): 101-147.
Capitanu L, Badita L-L, Florescu V. Stability Loss of the Cemented Stem of Hip Prosthesis due to Fretting Corrosion Fatigue. Tribol Ind 2017; 39(4): 536-546.
De Baets T, Waelput W, Bellemans J. Analysis of third body particles generated during total knee arthroplasty: Is metal debris an issue? The Knee. 2008; 15(2): 95-97.